In the part1 section of this tutorial series, I have taken time to explain how to set up Terraform to be working with AWS using AMI and creating a simple instance running as classic EC2.
This series aims to be a gentle walk-through of Terraform with full code available on git htttps://github.com/kdjomeda/intro-to-terraform.
In part 2, I will try to evolve the architecture a little bit and use a scenario that’s a bit close to reality. It will not be as detailed as in part1 and I will only highlight parts that I thought are important. The git branch for this part 2 is at https://github.com/kdjomeda/intro-to-terraform/tree/ec2-in-vpc
Creating a simple infra in a VPC
When you create a VPC from the wizard in AWS console a whole lot is done for you in the background. But when you are using the aws-cli to create it, it’s a bit more detailed compared to the console, but it gives you more control over the network. We will be creating a VPC with 2 public and 3 private subnets. Below are the VPC components to explicitly create when using CLI:
- Network Address range
- Subnet and their range
- Internet Gateway
- Optionally a Nat Gateway
- A routing table and its route for public traffic
- A routing table and its route for private traffic
- Routing table and subnets association
Our network CIDR will be 10.10.0.0/16 and below are the subnets we will be creating:
- public subnet in AZ A. cidr: 10.10.0.0/24
- public subnet in AZ B. cidr: 10.10.2.0/24
- private subnet in AZ A. cidr: 10.10.10.0/24
- private subnet in AZ B. cidr: 10.10.11.0/24
- private subnet in AZ C. cidr: 10.10.12.0/24
Creating the VPC
To create our subnets in different availability zones, we are going to need to use the hashicorp aws_availability_zones data source to pull the data from AWS
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
# main.tf /** Using Terraform data source of type aws_availability_zones to pull the availability zones (AZs) that available in our AWS region. */ data "aws_availability_zones" "azones" {} /** Creating our vpc with it's IP range. We enabled a vpc dns support We also enabled the dns hostname support Tags are also used to map the resource with specific groupings */ resource "aws_vpc" "terraform_vpc" { cidr_block = "10.10.0.0/16" enable_dns_hostnames = true enable_dns_support = true tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_vpc" // this Name tag is what is displayed as name of the VPC Env = "tutorial" Product = "handson" Terraform = true } } |
Creating the Internet Gateway
For our network to be accessible from internet we need to create an internet gateway in the vpc. We referred to the vpc id by using a resource interpolation [type(ie aws_vpc)].[name(terraform_vpc)].[attribute(id)]
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
#main.tf //.... /** Creating an aws internet gateway to allow communicationn between the vpc and internet We launched it in the vpc using its id */ resource "aws_internet_gateway" "terraform_igw" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.terraform_vpc.id //This is a reference to the id of VPN which is known at runtime tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_vpc_igw" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } |
Creating the Elastic IP to be used on the Nat Gateway
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
#main.tf //.... /** This is the IP that will be attached to our NAT Gateway for outbounds calls for nodes in private subnets */ resource "aws_eip" "terraform_nat_eip" { vpc = true tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_nat_iep" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handson" Terraform = true } } |
Creating a route table with a public route
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
#main.tf //.... resource "aws_route_table" "terraform_public_route_table" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.terraform_vpc.id tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_public_rtable" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } /** Creating a public route in the public route table This uses the internet gateway created above */ resource "aws_route" "terraform_public_route" { route_table_id = aws_route_table.terraform_public_route_table.id destination_cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0" gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.terraform_igw.id } |
Creating subnets and making it public
When creating a subnet in a vpc, unless you assign it a route table that has a public route, it can’t really be called public subnet
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
#main.tf //.... /** Creating a subnet with it's IP range In our VPC using its id. Assigning the first availability name from our AZs data source to its AZ name. Note though its name says so,there is nothing public or private about it */ resource "aws_subnet" "terraform_public_subnet_a" { cidr_block = "10.10.0.0/24" vpc_id = aws_vpc.terraform_vpc.id availability_zone = data.aws_availability_zones.azones.names[0] map_public_ip_on_launch = true tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_public_subnet_a" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } /** Creating a subnet with it's IP range In our VPC using its id. Assigning the second availability name from our AZs data source to its AZ name. Note though its name says so,there is nothing public or private about it */ resource "aws_subnet" "terraform_public_subnet_b" { cidr_block = "10.10.1.0/24" vpc_id = aws_vpc.terraform_vpc.id availability_zone = data.aws_availability_zones.azones.names[1] map_public_ip_on_launch = true tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_public_subnet_b" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } /** Making public subnet A actually public by associating it with the public route table */ resource "aws_route_table_association" "terraform_public_subnet_a_rtable_assoc" { route_table_id = aws_route_table.terraform_public_route_table.id subnet_id = aws_subnet.terraform_public_subnet_a.id } /** Making public subnet B actually public by associating it with the public route table */ resource "aws_route_table_association" "terraform_public_subnet_b_rtable_assoc" { route_table_id = aws_route_table.terraform_public_route_table.id subnet_id = aws_subnet.terraform_public_subnet_b.id } |
Creating a NAT Gateway
For the NAT Gateway to do its work, it has to be located in a place where it has internet access itself. That’s why it wasn’t created immediately after the internet gateway was created. It needs to live inside a public subnet
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
/** Creating the NAT Gateway in a public subnet for it to have access to internet through the Internet Gateway */ resource "aws_nat_gateway" "terraform_nat_gtw" { allocation_id = aws_eip.terraform_nat_eip.id subnet_id = aws_subnet.terraform_public_subnet_a.id } |
Creating a route table with private route
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
#main.tf //... resource "aws_route_table" "terraform_private_route_table" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.terraform_vpc.id tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_private_rtable" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } /** Creating a private route towards internet This uses the nat gateway created above */ resource "aws_route" "terraform_private_route" { route_table_id = aws_route_table.terraform_private_route_table.id nat_gateway_id = aws_nat_gateway.terraform_nat_gtw.id destination_cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0" } |
creating subnets and making them private
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 |
#main.tf //... /** Creating a subnet meant to be associated with our private route table Making it a private subnet in the AZ index 0 thus AZ A */ resource "aws_subnet" "terraform_private_subnet_a" { cidr_block = "10.10.10.0/24" vpc_id = aws_vpc.terraform_vpc.id availability_zone = data.aws_availability_zones.azones.names[0] tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_private_subnet_a" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } /** Making private subnet A actually private by associating it with the private route table */ resource "aws_route_table_association" "terraform_private_subnet_a_rtable_assoc" { route_table_id = aws_route_table.terraform_private_route_table.id subnet_id = aws_subnet.terraform_private_subnet_a.id } /** Creating a subnet meant to be associated with our private route table Making it a private subnet in the AZ index 0 thus AZ A */ resource "aws_subnet" "terraform_private_subnet_b" { cidr_block = "10.10.11.0/24" vpc_id = aws_vpc.terraform_vpc.id availability_zone = data.aws_availability_zones.azones.names[1] tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_private_subnet_b" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } /** Making private subnet B actually private by associating it with the private route table */ resource "aws_route_table_association" "terraform_private_subnet_b_rtable_assoc" { route_table_id = aws_route_table.terraform_private_route_table.id subnet_id = aws_subnet.terraform_private_subnet_b.id } /** Creating a subnet meant to be associated with our private route table Making it a private subnet in the AZ index 0 thus AZ A */ resource "aws_subnet" "terraform_private_subnet_c" { cidr_block = "10.10.12.0/24" vpc_id = aws_vpc.terraform_vpc.id availability_zone = data.aws_availability_zones.azones.names[2] tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_private_subnet_c" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } /** Making private subnet C actually private by associating it with the private route table */ resource "aws_route_table_association" "terraform_private_subnet_c_rtable_assoc" { route_table_id = aws_route_table.terraform_private_route_table.id subnet_id = aws_subnet.terraform_private_subnet_c.id } |
Creating an EC2 instance in the VPC
This time along, I will be using an Ubuntu node that I normally use for my production workload. Here the same principle applies. You need a security group, a public ssh key, etc. But since we want to create the instance inside a VPC, the security group obviously should be created in that same VPC. The Id of the subnet we want the node to be created in is used and the attribute we used for assigning the security_group in part 1 of this series is different from the vpc_security_group_ids used now.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 |
<# main.tf //..... /** Creating an security group allowing aside from the standard ssh port, http and http ports. */ resource "aws_security_group" "terraform_app_sec_group" { name = "terraform_app_db_sec_group" description = "simple Security Group for the single node" vpc_id = aws_vpc.terraform_vpc.id ingress { from_port = 80 to_port = 80 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] description = "opening http port to the world" } ingress { from_port = 443 to_port = 443 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] description = "opening https port to the world" } ingress { from_port = 22 // port to allow connection from ie to allow port range such as 20-26. this will be 20 to_port = 22 // port to allow connection to ie to allow port range such as 20-26. this will be 26 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] // This opens the node to the world. This is not good for production systems description = "allow connection to ssl port" } egress { // most of the time the egress is always needed. Here you can restrict the node out bound connection from_port = 0 protocol = "-1" to_port = 0 cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_db_sec_group" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } /** Uploading the public key of our generated ssh key pair with the name MyIdentity.pem */ resource "aws_key_pair" "my-identity-pem" { public_key = "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAQC8YsFK22z0OAJ1YdsBESQDnwJxTb/36EN1Zeymo2CksmPtURxp524nud0cI6uBCsCAgsYXaT3p7ijtmkDKA8tnIWr9pjfswUByUaJPKhnxp2r/V16U/VjgDs0RyTxQ0lo+hoy0OUVgapw9cXrtGBPukAT4qRVe8JLM7FDEMmGu8pkntgBbFneuj84YTHR4jcLzpF1FdoS+88ks9Oaw76bVlvJfLEeSDV7xdvF8IXqMznfoLPfe0gP0PTJ+bmLYwXfjlP7CUPPYEKG1sQHGEcKCs81QyncK6IwKSTwnpZX4YD/m45Yi0xi22tqI4qJ4oSN8Q2hNoAhS3/gCZXd6AiKDVJoVe6gQ5QpfCA+ZP21AH6z0T6HmPSvu6dbCm+qDfDGckysqwQBpHQANMLhWDEA7uVjr9Wpgyx60H1oCl2zYW40kcwBqO2i4tqQ+BnpZBgEPTn8DA0rn8LcfTNS/blrDIfJTYuYgW8HnCeT8hshelbux9B2YhAQE3AF1hQzFlgu23RHDcRHNQemkC20f4C8RAZcoY6ET99Xe+Ke46bHUcqOMK3oLKcCKfER3HLDHdAnaw5hJ2qkQEnDfYGBRCSRfetM0sCB7f3peYoH7WyTSR0/Qhn5iDWdjTqeopcIDY4KwEqag6rm3evLawnarUxnkvM6ez+A0OVTiUn7ZcndCTw== AWS Tutorial Usage" key_name = "MyIdentity.pem" } /** Creating a VM inside a VPC using a security group created within the VPC But more importantly using the subnet id of the subnet we want the node to be created in. Special notice on the subnet_id and the vpc_security_groups_ids */ resource "aws_instance" "terraform_ec2_instance" { ami = "ami-085925f297f89fce1" instance_type = "t2.nano" associate_public_ip_address = true // This allows the AWS to assign a public IP to the nonde vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.terraform_app_sec_group.id] key_name = aws_key_pair.my-identity-pem.key_name subnet_id = aws_subnet.terraform_public_subnet_b.id tags = { Name = "handson_tutorial_terraform_app_instance" Env = "tutorial" Product = "handons" Terraform = true } } |
Creating the infrastructure
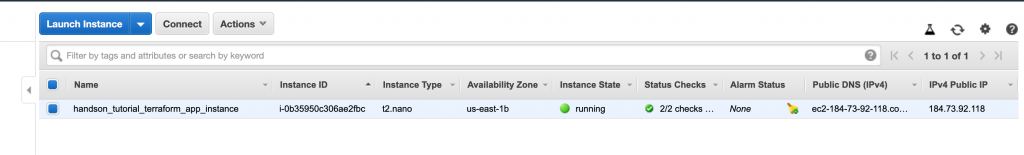
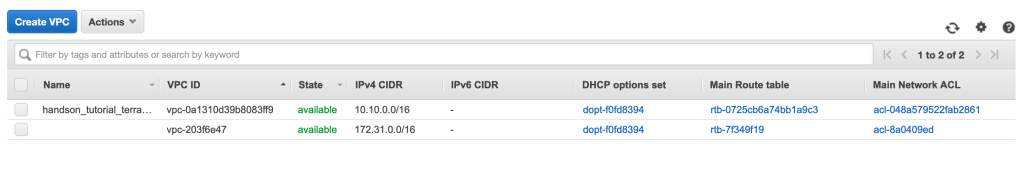
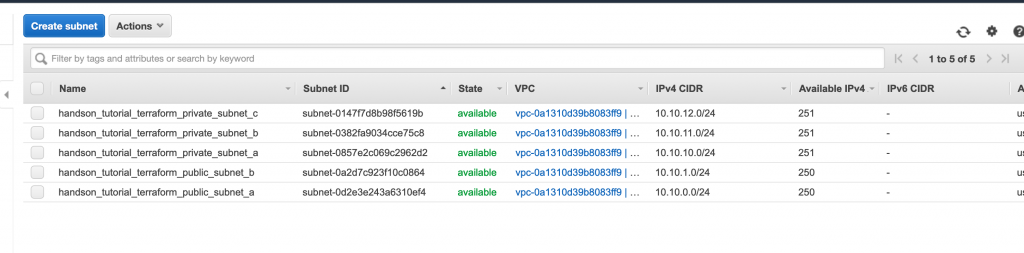
A quick terraform apply command and we should be up and running in no time and our instance and our vpc should look like the following: